
NADH, superoxide and amino acid metabolism are also altered in cancer. 8 Cancer cells have relatively high rates of aerobic glycolysis. For example, strains with mutations in a number of genes with activity in central carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism are also sensitive to doxorubicin.Īltered metabolism is a hallmark of cancer. Several other activities are also important in providing doxorubicin resistance. Mutants lacking DNA repair activities are sensitive to doxorubicin, consistent with its DNA damaging activities. cerevisiae leads to enhanced doxorubicin toxicity, suggesting the response to doxorubicin requires numerous cellular activities. Deletion mutation of 5–10% of non-essential genes (over 400) in S. 6,7 These screens have identified dozens of mutants with increased sensitivity to doxorubicin. cerevisiae strains harbouring deletions in all non-essential genes have been screened for sensitivity to doxorubicin. Genetic approaches to understand the mechanism of doxorubicin cytotoxicity have been very informative.
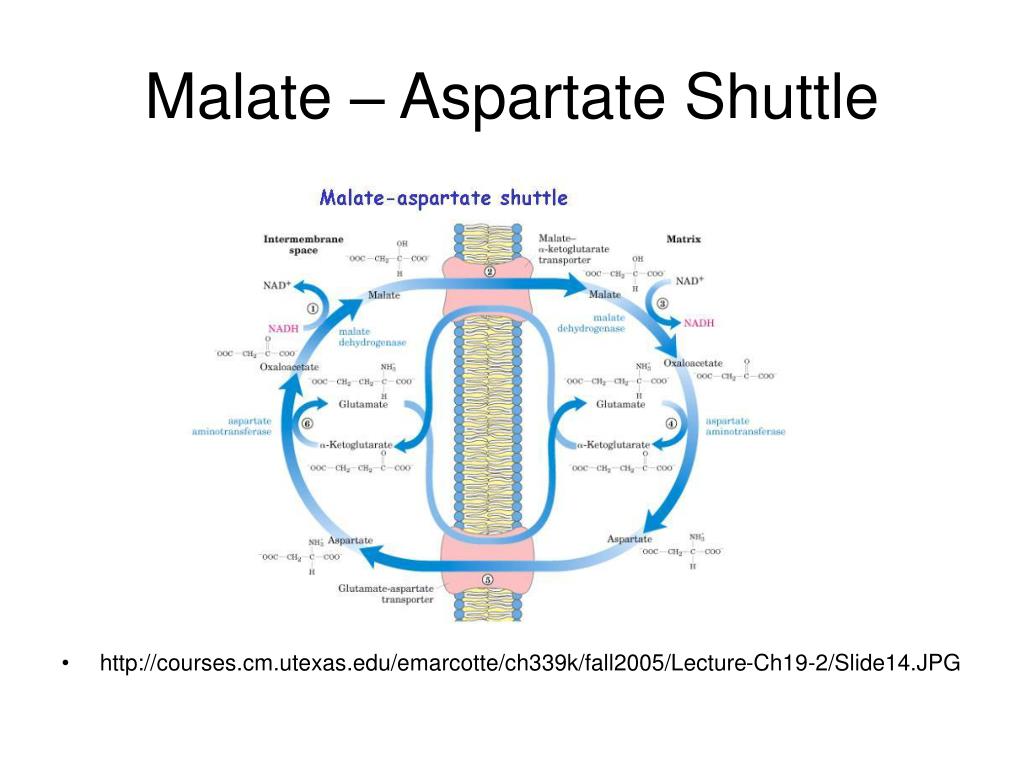
5 Understanding how these activities differentially affect normal and cancer cells is critical to improving the therapeutic ratio of doxorubicin. 4 Doxorubicin can also lead to death by mitotic catastrophe at low doses. 3 Doxorubicin has been proposed to induce apoptosis through increased ceramide synthesis and proteolytic activation of the transcription factor CREB3L1. 2 In addition, doxorubicin has redox activity and is able to oxidize NADH, effectively diverting electrons away from electron transport toward oxygen to create superoxide radicals. Doxorubicin creates DNA damage by intercalating into DNA, through topoisomerase II inhibition and possibly other means. Doxorubicin produces several effects in treated cells. Efforts to understand the mechanism of action of doxorubicin began with its discovery. Doxorubicin has become a widely used cancer chemotherapy drug and is part of standard therapy for breast cancer, lymphoma, sarcoma, thyroid cancer and many others. 1 Doxorubicin was subsequently isolated from a mutant of S. These data suggest glycolysis becomes less active and mitochondrial respiration more active following doxorubicin exposure.ĭaunorubicin is an anthracycline compound originally isolated from a soil bacteria, Streptomyces peucetius, near Apulia, Italy and found to have anticancer activity. Aspartate provides less protection from doxorubicin in cells mutant in either mitochondrial citrate synthase ( CIT1) or NADH oxidase ( NDI1), suggesting aspartate reduces doxorubicin toxicity by facilitating mitochondrial function. Aspartate supplementation allowed cultures exposed to doxorubicin in minimal media to arrest after one division with a budding pattern and survival comparable to cultures exposed in rich media. Cultures exposed to doxorubicin in minimal media arrested growth with no apparent cell cycle progression. Cell cycle response was assessed by examining the budding pattern of treated cells. Supplementing minimal media with aspartate, glutamate or alanine reduced doxorubicin toxicity. cerevisiae cultures exposed to doxorubicin in minimal media showed significantly more toxicity than cultures exposed in rich media. cerevisiae with mutations in pathways utilizing aspartate and other metabolites were examined for sensitivity to doxorubicin. cerevisiae were treated with doxorubicin in combination with a variety of amino acid supplements. This work examines the effect of amino acid metabolism on doxorubicin toxicity. cerevisiae have identified numerous mutants in amino acid and carbon metabolism which express increased doxorubicin sensitivity.
Genomic screens of doxorubicin toxicity in S.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
